How are Chemical Compounds Named?
Chemical nomenclature is the process of naming compounds. Naming compounds is important to allow scientists to identify and recognize the different compounds. When naming molecular compounds prefixes are used to dictate the number of a given element present in the compound. For example:
- “mono-” indicates one,
- “di-” indicates two,
- “tri-” is three,
- “tetra-” is four,
- “penta-” is five,
- “hexa-” is six,
- “hepta-” is seven,
- “octo-” is eight,
- “nona-” is nine,
- and “deca” is ten.
For a more in depth explanation check out this video.
How do you know whether to use 'ide' or 'ate', when naming a compound?
-ide is used for non-metal compounds generally. For example, Chlorine forms a chloride ion, so NaCl is Sodium Chloride. -ate and -ite are commonly used for polyatomic ions of Oxygen. -ate is used for the ion that has the largest number of Oxygen atoms. The -ite would be used for the ion with the smaller. NO2 and NO3 are known as Nitrite and Nitrate respectively. Nitrite has a smaller number of oxygen atoms so when added to an element it will be _ Nitrite. On the other than, Nitrate has a larger number of Oxygen atoms so when added to an element it is _ Nitrate Share your tips and advice for learning the names of chemical compounds in the comments.
How do you name compounds in chemistry?
The elements that are joined together through chemical bonds are known as chemical compounds. The chemical bonds between the compounds are strong enough to make them act like a single substance. Do you know how many compounds are there? The answer is that there are more than 350,000 chemical compounds that are registered for use and production. You can easily search the list of compounds online. The properties of compounds are different than those of the elements that were used to make those compounds. Now, the question arises how these compounds are named in chemistry? The answer is simple. There is a standard method of naming chemical compounds that is employed by all the scientists worldwide.
Rules for Naming Ionic or Molecular Compounds
Here are the simple steps to name compounds in chemistry: Step 1: Determine whether the compound in an ionic or molecular compound The first step is to identify whether the compound you are going to name is an ionic compound or a molecular compound. To do so, you should know what ionic and molecular compounds are.
- The compound is ionic if it contains a metal. Metals are present on the middle and left side of the periodic table.
- The compound is molecular if it contains two nonmetals. Nonmetals are present on the right side of the periodic table above the staircase, including hydrogen)
Step 2: To the end of the second compound's name, add the word "ide" After you have determined a molecular or ionic compound, the next step if to look at the second compound and replace the last three words with "ide". This rule is same for molecular or ionic compounds. For instance, if the second compound is chlorine, then you should remove "ine" and replace it with "ide", so that we can spell it "chloride". Step 3: Check if you require roman numerals Look for an ionic compound that has a transition metal that becomes a multivalent ion. If you have ionic compounds with transition metals, then you should add a roman numeral after the metal name to show the transition metal's charge. For instance, FeCl is named as iron (I) chloride and  is named as iron (II) chloride. Step 4: Check if any prefixes are required Because there are no ionic charges to balance out molecular compounds, therefore you should use prefixes shown in the table below:
is named as iron (II) chloride. Step 4: Check if any prefixes are required Because there are no ionic charges to balance out molecular compounds, therefore you should use prefixes shown in the table below:
| mono | 1 |
| di | 2 |
| tri | 3 |
| tera | 4 |
| penta | 5 |
| hexa | 6 |
| hepta | 7 |
| octa | 8 |
| nona | 9 |
| deca | 10 |
For instance,

is named as carbon dioxide and CO is named as carbon mono oxide.
Naming Ionic Compounds that Contain Polyatomic Ions
The rules for naming ionic compounds containing polyatomic ions are different. Polyatomic ions contain more than one atom. For instance, 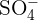 has one nitrogen atom and four oxygen atoms. In a polyatomic ion, the atoms are generally covalently bonded to each other. They act as a single charged unit. Most of the compounds containing polyatomic ions end with "ate" or "ite". Only some of them end with "ide". For instance,
has one nitrogen atom and four oxygen atoms. In a polyatomic ion, the atoms are generally covalently bonded to each other. They act as a single charged unit. Most of the compounds containing polyatomic ions end with "ate" or "ite". Only some of them end with "ide". For instance, 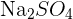 is named as sodium sulphate and
is named as sodium sulphate and 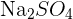 is called sodium sulphite.
is called sodium sulphite.
Naming Acids
The prefix "hydro" and the suffix name"ic" are used to name hydro acids. For instance, HF is called hydrofluoric acid and HCl is named as hydrochloric acid. Oxoacids are acids that contain oxygen. We use the suffix "ic" or "ous" while naming them. The suffix "ic" is used when the acid has more oxygen atoms. For instance,  is named sulphuric acid.
is named sulphuric acid.
What are the three types of compounds?
We all know that a chemical element has one type of atom only. When a substance contains more than one kind of atom, then we say that it is a compound. In other words, we can say that a compound refers to a substance in which two or more atoms are bonded with each other.
Millions of compounds exist and all fall in the following three broad categories:
1) Ionic Compounds These compounds are made up of ions. Ions are charged particles that are made when an atom gains or loses electrons. There are two types of ions: cation and anion. A cation is a positively charged ion and the anion is a negatively charged ion. These compounds are generally formed by a reaction between a metal and a nonmetal. To determine how to name these compounds, see the rules for naming ionic compounds in the previous section. 2) Molecular or Covalent Compounds They are formed when elements of the compound share electrons in a covalent bond to make up a molecule. These compounds are formed by the reaction between two nonmetals. 3) Acids Acids are compounds that contain hydrogen. It is easy to recognize acids as they contain hydrogen and anion. For instance, 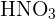 is named as nitric acid and
is named as nitric acid and  is named as sulphuric acid.
is named as sulphuric acid.
How do you identify types of compounds?
You can identify the type of compound by simply looking at the nature of its composition. Ionic Compounds: These compounds are formed when metal and non-metal are joined together. If you see that a compound is made from a metal and nonmetal, then you can easily categorize it as an ionic compound. For instance, NaCl is an ionic compound because sodium is a metal and chlorine is a nonmetal. Covalent compounds: These compounds are formed when two nonmetals are held together by a covalent bond. When you see a compound with two or more nonmetals, then you can easily term it as a covalent compound. For instance, carbon monoxide is made from two nonmetals carbon and oxygen, hence it is a covalent compound Acids: Acids contain hydrogen and anion.
What are the general rules for nomenclature? What are nomenclature rules?
Scientists employ nomenclature to name compounds clearly in chemistry. Ionic and molecular compounds are named using distinct methods. Nomenclature in chemistry refers to a set of rules to generate systematic names of compounds. The nomenclature which is used by the chemists and scientists worldwide is created and developed by the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry).
Rules for Nomenclature
A) Binary ionic compounds are made up of metal and non-metal. While naming the compound, the name of the metal is written first, followed by the name of the non-metal. The last three alphabets of the non-metal are replaced with "ide". B) If the compound contains polyatomic ion, then the last three alphabets of a non-metal are replaced with "ate" or "ite". "ate" is employed when there are more oxygen atoms present in a compound and "ite" is used when number of oxygen atoms present in a compound is less. Some compounds also contain "ide" for instance OH (hydroxide). C) To name binary compounds between two nonmetals, prefixes such as 1 = mono, 2 - di, 3 = tri, and so on are used. For instance,  is named as carbon dioxide and CO is named as carbon monoxide.
is named as carbon dioxide and CO is named as carbon monoxide.
Why is nomenclature important? What is the purpose of nomenclature?
There are two objectives of using nomenclature in chemistry:
- To make sure that a spoken or written chemical name does not contain any ambiguity regarding the chemical compound the name is referring towards. It is important that each chemical name points towards a single substance.
- To ascertain that each substance has one name only (although alternative names are acceptable in some cases)
- To help the chemists communicate with their peers easily.


 is named as iron (II) chloride. Step 4: Check if any prefixes are required Because there are no ionic charges to balance out molecular compounds, therefore you should use prefixes shown in the table below:
is named as iron (II) chloride. Step 4: Check if any prefixes are required Because there are no ionic charges to balance out molecular compounds, therefore you should use prefixes shown in the table below:  is named as carbon dioxide and CO is named as carbon mono oxide.
is named as carbon dioxide and CO is named as carbon mono oxide.
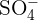 has one nitrogen atom and four oxygen atoms. In a polyatomic ion, the atoms are generally covalently bonded to each other. They act as a single charged unit. Most of the compounds containing polyatomic ions end with "ate" or "ite". Only some of them end with "ide". For instance,
has one nitrogen atom and four oxygen atoms. In a polyatomic ion, the atoms are generally covalently bonded to each other. They act as a single charged unit. Most of the compounds containing polyatomic ions end with "ate" or "ite". Only some of them end with "ide". For instance, 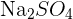 is named as sodium sulphate and
is named as sodium sulphate and  is named sulphuric acid.
is named sulphuric acid. 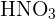 is named as nitric acid and
is named as nitric acid and