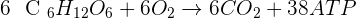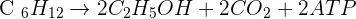Oxygen is one of the basic needs for life but ever wondered what is the role of oxygen in our body? Why it is so important to intake oxygen? That is why we dedicated this specific resource to teach you how plants utilize oxygen and what happens if they don't have oxygen?
What is Aerobic Respiration?
Let's start with the easiest ones. The term "Aerobic Respiration" refers to a set of reactions that takes place because of oxygen. Thanks to oxygen, the chemical energy will be converted to ATP (Adenosine triphosphate). The purpose of ATP is to carry the energy in a cell. In some books, it is also called an energy currency for a cell. Without ATP, a cell will die and that is why plants do aerobic respiration to make sure that their cells are full of energy for other purposes. All living things carry out aerobic respiration in order to live. We will talk about it in detail in the upcoming section how it converts chemical energy into ATP.
What is Anaerobic Respiration?
It is the opposite of aerobic respiration. The word, "Anaerobic" means without oxygen. In simple words, a series of metabolic reactions occur without the utilization of oxygen. Does that mean the cell will not generate any kind of energy? No, it will still provide energy but in a very less quantity. Plants do undergo anaerobic respiration too. Honestly, there are not so many reactions in anaerobic respiration but they do provide very quick energy to the cell in large amounts. Plants and microorganisms are the best examples of anaerobic respiration. Many microorganisms contain sulfate  in the transport chain (at their end) however, some of them uses nitrate
in the transport chain (at their end) however, some of them uses nitrate 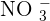 .
.
Process of Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
The process of both respiration starts when chloroplast makes glucose using solar energy. This process is known as photosynthesis. The glucose molecule contains 6 carbons, 12 hydrogens, and 6 oxygen atoms. The chemical formula of glucose is  . Glucose is food for plants. This molecule undergoes a series of reactions that will convert glucose into 38 ATPs. Although, approximately, 40 ATPs are produced the respiration process consumes 2 ATP of its own and that is why 38 ATPs are formed. Glucose undergoes a reaction called "Glycolysis" that converts glucose molecules into pyruvic acid. One molecule of glucose produces 2 molecules of pyruvic acid. This is the first phase of both, aerobic and anaerobic respiration. This reaction also releases two more things, 2 ATP as well as
. Glucose is food for plants. This molecule undergoes a series of reactions that will convert glucose into 38 ATPs. Although, approximately, 40 ATPs are produced the respiration process consumes 2 ATP of its own and that is why 38 ATPs are formed. Glucose undergoes a reaction called "Glycolysis" that converts glucose molecules into pyruvic acid. One molecule of glucose produces 2 molecules of pyruvic acid. This is the first phase of both, aerobic and anaerobic respiration. This reaction also releases two more things, 2 ATP as well as  . Let's keep track of ATPs and
. Let's keep track of ATPs and 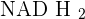 because they are very important, glycolysis produces pyruvic acid with 2 ATPs and
because they are very important, glycolysis produces pyruvic acid with 2 ATPs and  . From this phase, aerobic respiration separates from anaerobic respiration. Do note that the process of glycolysis consumes 2 ATP.
. From this phase, aerobic respiration separates from anaerobic respiration. Do note that the process of glycolysis consumes 2 ATP.
For Aerobic Respiration
For Aerobic respiration, there are two conditions, and both need to be fulfilled. If one of them doesn't fulfil then there will be no aerobic respiration. The first condition is pretty simple, there should be oxygen for aerobic respiration. The second condition is the requirement of mitochondria. The above picture shows mitochondria. Once the pyruvic acid enters perimitochondrial space (intermembrane space), it converts to acetyl coenzyme A (Acetyl Co-A). This reaction only occurs in this region because the enzyme that converts pyruvic acid to Acetyl Co-A is available in this space only. This reaction will release 2 more 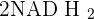 . Till now, we have 2 ATPs and
. Till now, we have 2 ATPs and 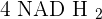 . Now Acetyl Co-A will be transferred to the matrix of mitochondria where the most important reaction occurs which is known as the Krebs cycle. The Krebs cycle will release
. Now Acetyl Co-A will be transferred to the matrix of mitochondria where the most important reaction occurs which is known as the Krebs cycle. The Krebs cycle will release 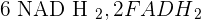 and 2 GTP (Guanosine-5'-triphosphate). GTP plays a very important role in the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. It is used as an energy source that binds the amino-bound tRNA to the A site of the ribosome. Since it is also an energy source, we can say that GTP is equal to ATP for this case, which means Krebs cycle produced
and 2 GTP (Guanosine-5'-triphosphate). GTP plays a very important role in the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. It is used as an energy source that binds the amino-bound tRNA to the A site of the ribosome. Since it is also an energy source, we can say that GTP is equal to ATP for this case, which means Krebs cycle produced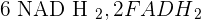 and 2 ATP. This is the second phase of aerobic respiration. After the Kreb cycle, we are left with 4 ATPs and
and 2 ATP. This is the second phase of aerobic respiration. After the Kreb cycle, we are left with 4 ATPs and  , and
, and 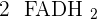 , the question is this process releases 38 ATPs, where are the remaining 34 ATPs? The answer is with the help of the cristae. The next step is to convert
, the question is this process releases 38 ATPs, where are the remaining 34 ATPs? The answer is with the help of the cristae. The next step is to convert 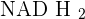 and
and  to ATPs and that is where the role of cristae starts. The process of converting
to ATPs and that is where the role of cristae starts. The process of converting 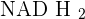 and
and  to ATPs is called Electron Transport System (ETS). Through this process,
to ATPs is called Electron Transport System (ETS). Through this process, 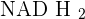 produces 3 ATPs, and
produces 3 ATPs, and  produces 2 ATPs. The whole process released
produces 2 ATPs. The whole process released  and
and 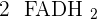 , let's calculate how much they are equivalent to ATPs.
, let's calculate how much they are equivalent to ATPs.  means 30 ATPs and
means 30 ATPs and 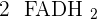 means 4 ATPs, all-together we have 34 ATPs. Let's calculate the total amount of ATPs produced in aerobic respiration. 2 ATPs were formed during the glycolysis, 2 ATPs were formed because of the Kreb cycle, and 34 ATPs were formed by converting
means 4 ATPs, all-together we have 34 ATPs. Let's calculate the total amount of ATPs produced in aerobic respiration. 2 ATPs were formed during the glycolysis, 2 ATPs were formed because of the Kreb cycle, and 34 ATPs were formed by converting 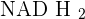 and
and  to ATPs in the cristae. If we sum up all the ATPs, we will get 38 ATPs and that is how aerobic respiration occurs.
to ATPs in the cristae. If we sum up all the ATPs, we will get 38 ATPs and that is how aerobic respiration occurs.
For Anaerobic Respiration
After the glycolysis reaction, we got pyruvic acid. Since there is an absence of either mitochondria or oxygen or even both, the products will be different and different amounts of ATPs will be produced. The pyruvic acid will turn into ethanol and carbon dioxide by utilizing the  . In the case of an animal cell, it will produce lactic acid. The glycolysis decomposes into pyruvic acid and doesn't require oxygen. It is already a part of anaerobic, therefore, the first phase will occur without any trouble. Let's count the ATPs produced in this respiration. Glycolysis produces 2 ATPs, and conversion of pyruvic acid to ethanol and carbon dioxide doesn't release any ATP, therefore, we are left we only 2 ATPs. In short, anaerobic respiration produces only 2 ATPs. If both, mitochondria and oxygen are present, then aerobic respiration will be preferred, however, in the absence of any of either of them will prefer anaerobic respiration.
. In the case of an animal cell, it will produce lactic acid. The glycolysis decomposes into pyruvic acid and doesn't require oxygen. It is already a part of anaerobic, therefore, the first phase will occur without any trouble. Let's count the ATPs produced in this respiration. Glycolysis produces 2 ATPs, and conversion of pyruvic acid to ethanol and carbon dioxide doesn't release any ATP, therefore, we are left we only 2 ATPs. In short, anaerobic respiration produces only 2 ATPs. If both, mitochondria and oxygen are present, then aerobic respiration will be preferred, however, in the absence of any of either of them will prefer anaerobic respiration.
What is the word equation for aerobic/anaerobic respiration?
Both processes have the same reactants but different products because of different conditions. In aerobic respiration, glucose will be broken into carbon dioxide and water.
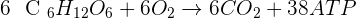
This is the overall equation of cellular respiration. This means that after reaction in cytoplast, mitochondria, and ETS, these are the products. After balancing the equation, it shows that six moles of glucose react with six moles of oxygen to release six moles of carbon dioxide and six moles of water with thirty-eight ATP. Below is the equation of anaerobic respiration.
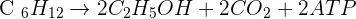
This might look simple but it isn't. Aerobic respiration goes through a series of metabolic reactions that should be talked about in detail. Each step in the aerobic reaction contains a lot of reactions that will be too much for this resource, let's just keep it simple for this one.
Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
Reaction with oxygen and without oxygen isn't the only difference in both respiration processes, they are a few more differences. Below is the table that shows the differences.
| Comparison Basis |
Aerobic Respiration |
Anaerobic Respiration |
| Products of the overall reaction |
Consumes six moles of glucose and oxygen to release six moles of carbon dioxide and water |
Consumes one mole of glucose and NADH to produce two moles of ethanol and two moles of carbon dioxide |
| Oxygen requirement |
This process requires oxygen |
This process doesn't require oxygen |
| Energy produced |
38 ATP worth energy is produced |
2 ATP worth energy is produced |
| Exchanging of gas |
Oxygen is absorbed and carbon dioxide is released |
No gas is absorbed, however, some gases are released depending on the microorganism |
| Place of reaction |
All metabolic reactions occur in the cytoplasm and mitochondria |
All reactions happen in the cytoplasm of the cell |
| Oxidation |
Complete oxidation process occurs converting carbohydrates into energy |
Because of the absence of oxygen, an incomplete oxidation process occurs. |
| Reaction time |
Since a lot of reaction occurs and a large amount of energy is been produced, it requires a lot of time |
Quick reactions |
| Occurs |
This process is found in all high living organisms |
It is mostly found in primitive prokaryotes. However, mammals also undergo this process during extreme movements |
Conclusion
The above process description is just a summary of aerobic and aerobic respiration. Aerobic and anaerobic respiration are very complex respiration processes. As a matter of fact, there is a huge process flow diagram of both of them with their intermediates that requires a lot of time to understand. Aerobic respiration is very common and found in many living things, however, anaerobic respiration is done on an industrial level for manufacturing ethanol and lactic acid. This domain is called biochemical engineering and let's talk about it next time.


 in the transport chain (at their end) however, some of them uses nitrate
in the transport chain (at their end) however, some of them uses nitrate 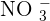 .
.  . Glucose is food for plants. This molecule undergoes a series of reactions that will convert glucose into 38 ATPs. Although, approximately, 40 ATPs are produced the respiration process consumes 2 ATP of its own and that is why 38 ATPs are formed. Glucose undergoes a reaction called "Glycolysis" that converts glucose molecules into pyruvic acid. One molecule of glucose produces 2 molecules of pyruvic acid. This is the first phase of both, aerobic and anaerobic respiration. This reaction also releases two more things, 2 ATP as well as
. Glucose is food for plants. This molecule undergoes a series of reactions that will convert glucose into 38 ATPs. Although, approximately, 40 ATPs are produced the respiration process consumes 2 ATP of its own and that is why 38 ATPs are formed. Glucose undergoes a reaction called "Glycolysis" that converts glucose molecules into pyruvic acid. One molecule of glucose produces 2 molecules of pyruvic acid. This is the first phase of both, aerobic and anaerobic respiration. This reaction also releases two more things, 2 ATP as well as  . Let's keep track of ATPs and
. Let's keep track of ATPs and 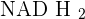 because they are very important, glycolysis produces pyruvic acid with 2 ATPs and
because they are very important, glycolysis produces pyruvic acid with 2 ATPs and 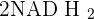 . Till now, we have 2 ATPs and
. Till now, we have 2 ATPs and 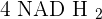 . Now Acetyl Co-A will be transferred to the matrix of mitochondria where the most important reaction occurs which is known as the Krebs cycle. The Krebs cycle will release
. Now Acetyl Co-A will be transferred to the matrix of mitochondria where the most important reaction occurs which is known as the Krebs cycle. The Krebs cycle will release 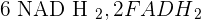 and 2 GTP (Guanosine-5'-triphosphate). GTP plays a very important role in the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. It is used as an energy source that binds the amino-bound tRNA to the A site of the ribosome. Since it is also an energy source, we can say that GTP is equal to ATP for this case, which means Krebs cycle produced
and 2 GTP (Guanosine-5'-triphosphate). GTP plays a very important role in the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. It is used as an energy source that binds the amino-bound tRNA to the A site of the ribosome. Since it is also an energy source, we can say that GTP is equal to ATP for this case, which means Krebs cycle produced , and
, and 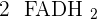 , the question is this process releases 38 ATPs, where are the remaining 34 ATPs? The answer is with the help of the cristae. The next step is to convert
, the question is this process releases 38 ATPs, where are the remaining 34 ATPs? The answer is with the help of the cristae. The next step is to convert  to ATPs and that is where the role of cristae starts. The process of converting
to ATPs and that is where the role of cristae starts. The process of converting